00:00-00:07
[Upbeat instrumental music plays; Humulin® R U-500 logo shows on screen; Lilly logo shows on screen]
Caption: Humulin® R U-500 insulin human injection 500 units/mL
Caption: Lilly
Caption: PP-HM-US-2040 07/2023 ©Lilly USA, LLC 2023. All rights reserved.
Caption: Chapters
1. Indication for Humulin® R U-500
2. U-500 Trial Design
3. Identifying the U-500 Patient
4. Efficacy Findings
5. Insulin Monotherapy
6. Hypoglycemia
7. Discussing Hypoglycemia
8. Initiation
9. Determining Starting Dose: BID or TID?
10. Titration
11. Starting With the U-500 KwikPen®
12. U-500 KwikPen® Features
13. Getting Patients Started
14. Affordability
15. At the Pharmacy
16. Important Safety Information
00:07-00:22
Caption: Chapter 1
Caption: Indication for Humulin® R U-500
Caption: Humulin® R U-500 is a concentrated human insulin indicated to improve glycemic control in adults and pediatric patients with diabetes mellitus requiring more than 200 units of insulin per day.
Caption: Limitations of Use: The safety and efficacy of Humulin R U-500 used in combination with other insulins, or when delivered by continuous subcutaneous infusion, has not been determined.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
00:22-00:30
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
00:30-00:51
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo appears on-screen]
Narrator: The Humulin R U-500 initiation trial was conducted to compare the efficacy and safety of U-500 dosed TID or BID in adult patients uncontrolled on high-dose U-100 insulins.
Caption: U-500 Trial Design
Caption: Chapter 2
Caption: The Humulin R U-500 Initiation Trial design
Caption: 24-week, open-label, randomized trial conducted in the United States and Puerto Rico
Caption: Compared TID (n=162) versus BID (n=163) for U-500 insulin to replace high-dose U-100 insulin
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500
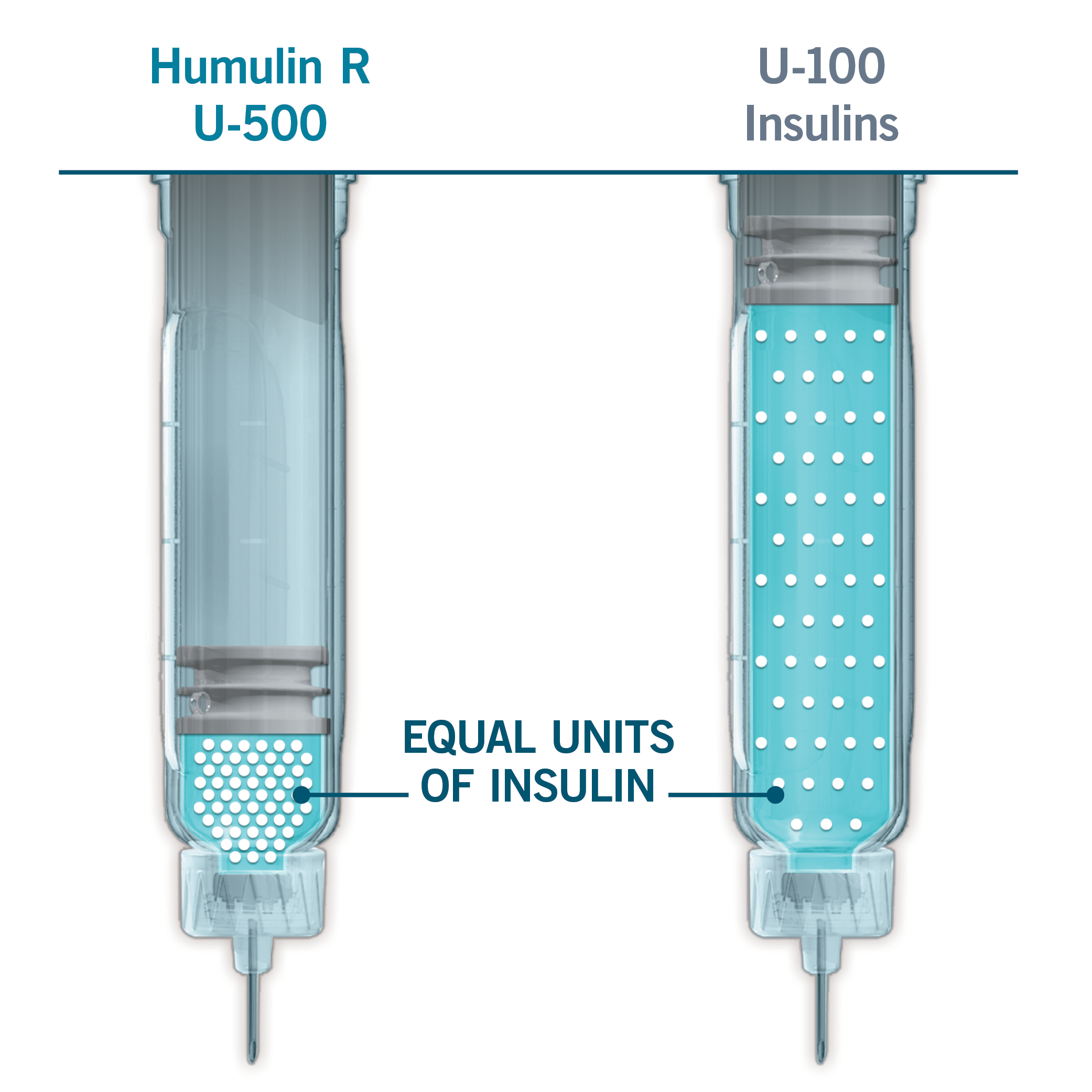
Caption: Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia, or Death Due to Dosing Errors With Vial Presentation
Caption: Can be life threatening. Overdose has occurred as a result of dispensing, prescribing, or administration errors, Attention to details at all levels is required to prevent these errors.
Caption: Patients should be prescribed U-500 syringes for use with Humulin R U-500 vials. Do not use any other type of syringe to administer Humulin R U-500.
Caption: If using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®, patients should be counseled to dial and dose the prescribed number of units of insulin.
Caption: Do NOT perform dose conversion when using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen or a U-500 insulin syringe.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
00:51-01:03
Narrator: In these patients who needed more than 200 units of insulin a day, would U-500 improve glycemic control with just two or three daily injections?
Caption: Trial participants:
Caption: Had an average A1C of 8.7%
Caption: Had been on basal-bolus analog regimens (~67%)
Caption: Injected 5 times a day (median; range 2-10)
Caption: Had a mean total daily insulin dose of 287.5 units
Caption: Additional Study Design Information
Caption: This trial included a 4-week lead-in period. This was followed by a 24-week treatment period divided into:
Caption: A 12-week intensified dose titration phase (visits weekly for 6 weeks, then every 2 weeks for 6 weeks)
Caption: A 12-week maintenance dose titration phase (visits every 3 weeks)
Caption: Randomization was stratified by baseline A1C (≤8% or >8%) and total daily insulin dose (TDD; ≤300 or >300 units).
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
01:03-01:28
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo appears on screen; Dr. Ralph Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: In my practice, patients that come in on large numbers of injections a day and large amounts of insulin a day are frustrated because they're taking a lot of medication and their A1C may be either stuck or going up, despite everything that they feel they are doing.
Caption: Identifying the U-500 Patient
Caption: Chapter 3
Caption: Ralph C. Goodman, MD; Endocrinologist; Sacred Heart Medical Group
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
01:28-01:40
[Dr. Rosemarie Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: A patient that may benefit from U-500 is usually a patient who is using high doses of insulin, meaning higher than 200 units per day in terms of total daily doses.
Caption: Rosemarie Lajara, MD, FACE; Endocrinologist; Diabetes Centers of America – DFW
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
01:40-01:55
Dr. Lajara: In addition, whose A1C is not controlled and their blood sugar readings are not controlled, they may also have higher body mass index and have signs and symptoms consistent with insulin resistance.
Caption: Uncontrolled A1C
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
01:55-02:07
[Dr. Lowell Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: These are patients who are doing all the right diabetic behaviors, checking their blood sugars, watching their diet, and taking all their injections they are supposed to be, but still not achieving the glycemic targets that we've set out for them.
Caption: Lowell Schmeltz, MD, FACE; Assistant Professor, Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine; Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism; Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
02:07-02:26
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: Patients really want to see an improvement in their A1C. They know that this is a marker of overall control. They know that it reflects the risk of complications, and they are really tuned in now to asking about their A1C on every visit, and they want the feedback that it's improving.
Caption: Lower A1C
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
02:26-02:38
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: As an endocrinologist, one of the biggest sources of frustration is that I have a metric by which I'm measured in terms of success of treatment recommendations, which is the A1C.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
02:38-03:09
[A patient sits in a doctor’s office at a desk, speaking with their healthcare provider; the HCP is explaining the Humulin pen, which the patient is holding in their hands; Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: And if the A1C is not dropping, despite increases in their daily doses of insulin, I start addressing what may be the factors influencing these numbers. I address technique. I address compliance. I address issues obtaining the insulin, co-pays, access, different things that may affect blood sugar control, including stressors, illnesses, new medications. There's a host of possibilities.
Caption: Models for illustrative purposes only
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
03:09-03:22
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: The frustration that patients feel and that their physicians that refer them feel is a real thing that I see. They are on a lot of units of insulin a day and their A1C may be going nowhere.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
03:22-03:40
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: When I introduce U-500 to a patient, it's usually in the context that you are not doing well in terms of your A1C readings and your blood sugar readings, and I see that you're taking several injections a day and that your total amount of insulin per day is quite high.
Caption: High doses of insulin
Caption: >200 units per day
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
03:40-04:02
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera; animated image of Humulin R U-500 KwikPen; the KwikPen spins slowly]
Dr. Goodman: I don't wait to start patients on U-500 if they are out of control on high doses of U-100 because they accept the change readily. They accept the simpler regimen, and when they start on U-500 and see the improvement and the control that's possible, I think it engages them to be even more active in trying to manage their diabetes.
Caption: Humulin® R U-500 KwikPen®
Caption: U-500 may reduce the number of daily injections compared to standard U-100 insulin. Most patients will require 2-3 injections of U-500 a day. Patients can inject up to 80% less liquid and still get the dose they need.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
04:02-04:23
Narrator: The primary outcome of the trial confirmed that Humulin R U-500 produced similar reductions in A1C levels when prescribed TID or BID. In both cases, the mean reduction was greater than 1% at endpoint.
Caption: Efficacy Findings
Caption: Chapter 4
Caption: Primary Outcome: Similar mean reductions in A1C between TID and BID at endpoint
Caption: Supporting Information
Descriptive Clue: This line graph presents the primary end point of similar reductions in A1C between a 3-times daily (n = 162) and 2-times daily (n = 161) dosing regimen for Humulin R U-500. The mean A1C at baseline for both groups was 8.7%. At 24 weeks, patients in the 3-times-daily arm of the study had a least squares mean change in A1C of -1.1% (A1C of 7.5%) and patients in the 2-times-daily arm had a least squares mean change in A1C of -1.2% (A1C of 7.4%). The difference in least squares mean A1C change from baseline between treatment groups was -0.10%. The 95% confidence interval (-0.33% to 0.12%) fell within the range established by the noninferiority margin of 0.4%, demonstrating clinical equivalence of the 2 treatment regimens. All efficacy analyses were conducted using the full analysis set defined as all randomized patients receiving at least 1 dose of study drug at baseline. The study was conducted with U-100 insulin syringes and Humulin R U-500 vials. The Humulin R U-500 Initiation Trial was a 24-week, open-label, randomized trial to compare the efficacy and safety of 2 dosing regimens (3 times daily, n = 162 vs 2 times daily, n = 163) for U-500 insulin replacing high-dose U-100 insulin (greater than 200 units per day) with or without oral antihyperglycemic drugs in adult patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. These regimens were found to be equivalent for A1C reduction over 24 weeks, and both were efficacious.
Caption: LS = least squares; MMRM = mixed-model repeated measures; TID = three times a day; BID = two times a day.
Caption: The difference in least squares mean (LSM) A1C change from baseline between treatment groups (BID vs TID) was -0.10%. The 95% CI (-0.33% to 0.12%) fell within the range established by the noninferiority margin (0.4%), demonstrating clinical equivalence of the two treatment regimens.
Caption: Mean A1C at baseline for both groups was 8.7%.
Caption: Mean A1C at endpoint was 7.5% for TID and 7.4% for BID
Caption: All efficacy analyses were conducted using the full analysis set defined as all randomized patients receiving at least one dose of study drug at baseline.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Dosing Errors
Caption: Extreme caution must be observed in measuring the dose of Humulin R U-500 because inadvertent overdose may result in serious adverse reaction or life-threatening hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
04:23-04:43
[A bar graph titled “Percentage of Patients Reaching Glycemic Targets at Endpoint” appears on screen]
Narrator: In addition, the number of trial participants reaching glycemic targets was measured. About 70% of patients were below 8%, approximately 50% were below 7.5%, and approximately 30% were below 7% at endpoint.
Descriptive Clue: This bar graph presents the percentage of patients reaching glycemic targets at end point (24 weeks for those not at target at randomization). The mean A1C for patients at baseline (TID and BID) was 8.7%. The percentages of patients at target at baseline were approximately 1.9% (A1C less than 7.0%), approximately 9.9% (A1C less than 7.5%), and approximately 24.8% (A1C less than 8.0%). Approximately 70% of patients taking Humulin R U-500 3 times daily and 69% of patients taking Humulin R U-500 2 times daily achieved an A1C less than 8.0%. Approximately 55% of patients taking Humulin R U-500 3 times daily and 47% of patients taking Humulin R U-500 2 times daily achieved an A1C less than 7.5%. Approximately 29% of patients taking Humulin R U-500 3 times daily and 31% of patients taking Humulin R U-500 2 times daily achieved an A1C less than 7.0%. NOTE: There was no statistically significant difference in the percent-to-target results achieved between 3-times-daily and 2-times-daily dosing regimens. All efficacy analyses were conducted using the full analysis set defined as all randomized patients receiving at least 1 dose of study drug at baseline.
Caption: Approximately 70% of patients reached A1C <8.0% at 24 weeks
Caption: Percentage of Patients Reaching Glycemic Targets at Endpoint*
Caption: Mean A1C at Baseline (TID & BID): 8.7%
Caption: NOTE: There was no statistically significant difference in percent-to-target results achieved between TID and BID dosing.
Caption: *At 24 weeks for those not at target at randomization. Patients at target (%) at baseline: and 24.8% (<8.0%); 9.9% (<7.5%); 1.9% (<7.0%)
Caption: All efficacy analyses were conducted using the full analysis set defined as all randomized patients receiving at least one dose of study drug at baseline.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500
Caption: Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia, or Death Due to Dosing Errors With Vial Presentation
Caption: Can be life-threatening. Overdose has occurred as a result of dispensing, prescribing, or administration errors. Attention to details at all levels is required to prevent these errors.
Caption: Patients should be prescribed U-500 syringes for use with Humulin R U-500 vials. Do not use any other type of syringe to administer Humulin R U-500.
Caption: If using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®, patients should be counseled to dial and dose the prescribed number of units of insulin.
Caption: Do NOT perform dose conversion when using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen or a U-500 insulin syringe.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
04:43-05:03
[Dr. Robert Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: The trial was designed to address a group of patients that are struggling with their diabetes. They're taking very high doses of insulin, given often with many injections daily, yet their A1C is still not controlled. So given the chance to develop a prospective trial looking at U-500 in the real world was a great opportunity.
Caption: Robert Hood, MD, FRCPC, FACE; Director, Endocrine Clinic of Southeast Texas; Clinical Investigator of the Humulin R U-500 Study
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
05:03-05:11
Dr. Hood: Imagine the frustration that you're taking more and more insulin, you're taking more and more injections, yet your A1C still remains elevated.
Caption: Elevated A1C
Caption: Insulin volume
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
05:11-05:23
Dr. Hood: So, to be able to switch onto just one type of insulin and see this greater than 1% reduction on the average is very heartening to a group of patients that are often very frustrated living with their diabetes.
Caption: Mean Reduction A1C (TID)* -1.1%
Caption: Mean Reduction A1C (BID)* -1.2%
Caption: *Measured at 24 weeks. All efficacy analyses were conducted using the full analysis set defined as all randomized patients receiving at least one dose of study drug at baseline.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
05:23-05:59
[Dr. Jeffrey Jackson talks to camera]
Caption: Jeffrey Jackson, MD, FACE, CDE
Dr. Jackson: A drop of more than 1.1% is a very significant drop in these patients. Also, the percent to target was important and so we saw about 70% get below an A1C of 8%. We saw 50% get below 7.5%, and we saw 30% get to A1C target less than 7%, and those are very good results, especially for this difficult-to-treat population.
Caption: 70% approximate value*: A1C <8.0%
Caption: 50% approximate value*: A1C <7.5%
Caption: 30% approximate value*: A1C <7.0%
Caption: *Results at endpoint. All efficacy analyses were conducted using the full analysis set defined as all randomized patients receiving at least one dose of study drug at baseline. At 24 weeks for those not at target at randomization. Patients at target (%) at baseline: 24.8% (<8.0%), 9.9% (<7.5%), and 1.9% (<7.0%).
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
05:59-06:28
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo appears on-screen; Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: When a patient is on a basal-bolus regimen and their blood sugars are not controlled, and they are already reaching over 200 units a day, that's an opportunity to discuss the burden of the number of injections, whether they're missing injections or not. Because obviously we know that the more times we ask a patient to do something, the more opportunities for them to miss a dose here and there.
Caption: Insulin Monotherapy
Caption: Chapter 5
Caption: Dr Rosemarie Lajara, Endocrinologist, Diabetes Centers of America – DFW
Caption: Injection Burden
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
06:28-06:49
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: We hear the phrase injection burden, and to me this means patients burn out on taking five or more injections a day to try to control their blood sugars. They forget or they are away from their home or don't have the insulin available to them. Plus, just the burden of taking a number of different injections makes their regimen more complicated.
Caption: Dr Ralph Goodman, Endocrinologist, Sacred Heart Medical Group
Caption: 5 or more injections
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
06:49-07:07
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: One of the things that's fairly interesting about U-500 insulin is that it has both basal and prandial components. And this actually allows us to use it as monotherapy insulin, in that it can provide both basal insulin and also very importantly some mealtime coverage as well.
Caption: Dr Robert Hood, Clinical Investigator of the Humulin R U-500 Study
Caption: Basal prandial properties
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
07:07-07:28
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: U-500 is different compared to a U-100 formulation in terms of its pharmacological properties. Interestingly enough, onset of action is about 30 minutes after injection, but it has a peak effect around four to six hours after being injected and a duration of up to 24 hours.
Descriptive Clue: A chart titled “Mean Insulin Activity vs Time Action Profiles After SQ Injection of a 100-Unit Dose of U-500*” shows the glucose infusion rate over 24 hours for a 100-unit dose of Humulin R U-500 in healthy obese subjects. The chart shows that Humulin’s mean glucose infusion rate hits its peak at 4 hours then tapers off, through 24 hours.Mean insulin activity vs Time Action Profiles after SQ Injection of a 100-unit Does of U-500. Median time-to-peak insulin concentration was six hours after administration via subcutaneous injection and longer duration of action.
Caption: *In healthy obese subjects.
Caption: The time-course action of any insulin may vary in different individuals or at different times in the same individual.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
07:28-07:50
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: For patients starting on Humulin R U-500 insulin monotherapy, it provides an opportunity to improve patient satisfaction on three levels. They're able to reduce the number of injections they're taking on a daily basis. They are able to reduce the amount of insulin by volume that they're taking on a daily basis. And probably just as important in today's society, they're able to reduce the number of co-pays.
Caption: Dr Lowell Schmeltz; Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism; Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Insulin Monotherapy
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: Fewer Injections*
Caption: 80% less volume
Caption: *U-500 may reduce the number of daily injections compared to standard U-100 insulin. Most patients will require 2-3 injections of U-500 a day. Patients can inject up to 80% less liquid and still get the dose they need.
Caption: Patients transitioning from U-100 basal-bolus therapy to U-500 as insulin monotherapy may have fewer co-pays
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
07:50-07:59
[Dr. Goodman talks to screen]
Dr. Goodman: Moving these patients to U-500 not only simplifies their regimen, but it improves their control and allows them to use one type of insulin only. I've been very satisfied with the basal and prandial control that I get with U-500, and that's evidenced in the response that I see in my patients.
Caption: Insulin Monotherapy
Caption: Simpler regimen
Caption: U-500 may reduce the number of daily injections compared to standard U-100 insulin. Most patients will require 2-3 injections of U-500 a day. Patients can inject up to 80% less liquid and still get the dose they need.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
08:08-08:33
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera; a patient converses with her HCP]
Dr. Lajara: When I tell my patients that they will go to just one insulin and less number of shots per day, they are elated. It's something in the disease state in which usually, once you start insulin, the norm is to go up and up and up, and more injections are added. Going down is a pleasant surprise for my patients.
Caption: Insulin monotherapy
Caption: Fewer injections
Caption: U-500 may reduce the number of daily injections compared to standard U-100 insulin. Most patients will require 2-3 injections of U-500 a day.
Caption: Data on file, Lilly USA, LLC. HI20130603A.
Caption: Data on file, Lilly Research Laboratories. HI20130221A.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: Models for illustrative purposes only
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
08:33-08:54
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo appears on-screen, then a table with text below and to the right of it appears]
Narrator: The trial also measured the hypoglycemia that participants experienced for TID and BID regimens. There was a similar rate and incidence of severe hypoglycemia between TID and BID treatment algorithms.
Caption: Hypoglycemia
Caption: Chapter 6
Caption: Table -- Rates and Incidence of Hypoglycemia in the Humulin R U-500 Initiation Trial
| | TID
(n = 162) | BID
(n = 161) |
| Severe hypoglycemia | | |
| Incidence, n (%) | 3 (1.9) | 6 (3.7) |
| 30-day event rate* | 0.004 ± 0.028 | 0.009 ± 0.053 |
| Nocturnal <50 mg/dL | | |
| Incidence, n (%) | 59 (36.4) | 79 (49.1) |
| 30-day event rate* | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.04 |
| Nocturnal ≤70 mg/dL | | |
Incidence, n (%) | 126 (77.8) | 130 (80.8) |
| 30-day event rate* | 0.92 ± 0.11 | 1.20 ± 0.13 |
Caption: *Events/patients/30 days.
Caption: Rates are geometric least squares means ± SE (documented symptomatic and nocturnal) or means ± SD (severe)
Caption: NOTE: During this trial, hypoglycemia was categorized as documented symptomatic, nocturnal, or severe hypoglycemia. Documented symptomatic hypoglycemia was defined as signs or symptoms associated with hypoglycemia and plasma glucose ≤70 mg/dL or <50 mg/dL. Nocturnal hypoglycemia was defined as documented symptomatic hypoglycemia occurring between bedtime and waking. By definition, severe hypoglycemia required assistance from another person for treatment and was accompanied by neurologic/cognitive impairment. Incidence is reported as the number of patients with at least one hypoglycemic episode.
Caption: All hypoglycemia analyses were performed using the full analysis set defined as all randomized patients receiving at least one dose of study drug.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500
Caption: Hypoglycemia
Caption: Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction associated with insulins, including Humulin R U-500. Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures, may be life-threatening, or cause death.
Caption: Increase monitoring with changes to insulin dosage, co-administered glucose-lowering medications, meal patterns, physical activity, and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment or hypoglycemia unawareness. To minimize risk of hypoglycemia, do not administer Humulin R U-500 intravenously or dilute or mix with other products, including other insulins.
Caption: Patients and caregivers must be educated to recognize and manage hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an essential role in the prevention and management of hypoglycemia. In patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and patients who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia, increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring is recommended.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
08:54-09:05
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: When designing the protocol, we definitely wanted to see an improvement in glycemic control, but we were also very respectful that these are difficult-to-treat patients with very high doses of insulin.
Caption: Dr Robert Hood, Clinical Investigator of the Humulin R U-500 Study
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
09:05-09:21
Dr. Hood: The severe hypoglycemia data is very important. There are some clinicians that think these patients are so insulin-resistant that they're just not going to get any hypoglycemia at all. Not only can they get hypoglycemia, they can certainly get severe hypoglycemia.
Caption: Severe hypoglycemia
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
09:21-09:39
Dr. Hood: During the trial, the incidence of severe hypoglycemia was 1.9% with the TID group and 3.7% with the BID group. Those differences were not statistically significant. And in my practice, it's acceptable from the standpoint of trying to get tighter glycemic control in insulin-requiring patients.
Caption: Hypoglycemia
Caption: 30-day incidence of severe hypoglycemia
Caption: TID: 1.9%
Caption: BID: 3.7%
Caption: No statistical difference
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
09:39-10:04
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: When patients start on U-500, it's definitely a balancing act. They're on a totally new regimen. Many of these patients have been out of control for years. So, I don't necessarily try to get them well controlled within four or six weeks. We're trying to ease their blood sugars down while avoiding hypoglycemia.
Caption: Discussing Hypoglycemia
Caption: Chapter 7
Caption: Dr Ralph Goodman, Endocrinologist, Sacred Heart Medical Group
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
10:04-10:24
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: When I start an insulin-containing regimen, I always discuss with my patients the potential for hypoglycemia. When I'm starting somebody on U-500, this discussion gets refreshed and I do go over signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and the importance of monitoring their sugars.
Caption: Dr Rosemarie Lajara, Endocrinologist, Diabetes Centers of America – DFW
Caption: Hypoglycemia: Signs, Symptoms, Monitoring Blood Sugar
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia, or Death Due to Dosing Errors With Vial Presentation
Caption: Can be life-threatening. Overdose has occurred as a result of dispensing, prescribing, or administration errors. Attention to details at all levels is required to prevent these errors. Patients should be prescribed U-500 syringes for use with Humulin R U-500 vials. Do not use any other type of syringe to administer Humulin R U-500. If using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®, patients should be counseled to dial and dose the prescribed number of units of insulin. Do NOT perform dose conversion when using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen or a U-500 insulin syringe.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
10:24-10:35
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: I just try to tell them that they will be at, you know, some risk with U-500, and I tell them to notify me if it's occurring or if they reach certain limits that I find unacceptable.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia, or Death Due to Dosing Errors With Vial Presentation
Caption: Can be life-threatening. Overdose has occurred as a result of dispensing, prescribing, or administration errors. Attention to details at all levels is required to prevent these errors. Patients should be prescribed U-500 syringes for use with Humulin R U-500 vials. Do not use any other type of syringe to administer Humulin R U-500. If using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®, patients should be counseled to dial and dose the prescribed number of units of insulin. Do NOT perform dose conversion when using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen or a U-500 insulin syringe.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
10:35-10:50
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: Especially in the first couple of weeks of initiation, we do emphasize the importance of self-monitoring and signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia in order for us to make adjustments based on the occurrence of these episodes.
Caption: Hypoglycemia signs and symptoms
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia, or Death Due to Dosing Errors With Vial Presentation
Caption: Can be life-threatening. Overdose has occurred as a result of dispensing, prescribing, or administration errors. Attention to details at all levels is required to prevent these errors. Patients should be prescribed U-500 syringes for use with Humulin R U-500 vials. Do not use any other type of syringe to administer Humulin R U-500. If using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®, patients should be counseled to dial and dose the prescribed number of units of insulin. Do NOT perform dose conversion when using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen or a U-500 insulin syringe.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
10:50-11:14
Dr. Lajara: In order to minimize hypoglycemia, I tend to lower the total daily dose of U-500 if the patient's A1C is below eight or their mean sugars are around 180. If the A1C is higher than eight and the sugars are high, higher than 200 for sure, then I stick with the total daily dose.
Caption: A1C ≤8% (or mean SMPG <183 mg/dL in the last 7 days) = 80% of total daily U-100 dose
Caption: A1C >8% (and mean SMPG ≥183 mg/dL in the last 7 days) = 100% of total daily U-100 dose
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia, or Death Due to Dosing Errors With Vial Presentation
Caption: Can be life-threatening. Overdose has occurred as a result of dispensing, prescribing, or administration errors. Attention to details at all levels is required to prevent these errors. Patients should be prescribed U-500 syringes for use with Humulin R U-500 vials. Do not use any other type of syringe to administer Humulin R U-500. If using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®, patients should be counseled to dial and dose the prescribed number of units of insulin. Do NOT perform dose conversion when using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen or a U-500 insulin syringe.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
11:14-11:42
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: Having data to support a titration algorithm with a reduction of 20% if their hemoglobin A1C is below 8% or a unit-for-unit conversion if their hemoglobin A1C is 8% or above is very reassuring as a clinician. Again, from a safety standpoint, making sure I'm not going to cause significant hypoglycemia, but also from a starting algorithm that we're going to improve glycemic control and then titrate from there.
Caption: Dr Lowell Schmeltz; Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism; Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: Ask your Lilly representative for more titration information or visit www.humulinhcp.com
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
11:42-12:06
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: I'll ask them to check their blood sugar three or four times a day. And occasionally I'll ask them to get up and check it in the middle of the night, especially during the initial dose titration period. They should eat at a regular basis, 30 minutes after their injections, and if there's any other change in their regimen that might affect their blood sugar, they need to let me know about it.
Caption: Check blood sugar 3 or 4x per day
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
12:06-12:18
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: So, having data supporting a titration algorithm with the main purpose of minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia and then a secondary goal of improving blood sugars is a wonderful tool to have.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
12:18-12:41
Dr. Schmeltz: Endocrinologists historically have had to convert patients over to U-500 using their clinical judgment without much data. Historically, some reduced 20%, some reduced 10% of the total daily insulin dose, and others have done a unit for unit conversion.
Caption: Initiation
Caption: Chapter 8
Caption: Lowell Schmeltz, MD, FACE; Assistant Professor, Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine; Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
12:41-13:13
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: One of the powerful things about this trial is we provided a conversion protocol and then we followed the patients subsequently to see how successful that was. So, the clinician now has data looking at what happens over the ensuing weeks. When designing the protocol, we definitely wanted to see an improvement in glycemic control, but we were also very respectful that these are difficult-to-treat patients with very high doses of insulin. So, the protocol was designed specifically to keep safety in mind.
Caption: Robert Hood, MD, FRCPC, FACE; Director, Endocrine Clinic of Southeast Texas; Clinical Investigator of the Humulin R U-500 Study
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
13:13-13:32
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: This study showed us that with patients with a hemoglobin A1C under 8%, we should reduce the total daily dose of insulin by 20%. But for those patients with a hemoglobin A1C over 8%, doing a unit for unit total daily dose insulin conversion was effective and also minimized the risk of hypoglycemia.
Caption: A1C ≤8% = 80% of total daily U-100 dose
Caption: A1C greater >8% = 100% of total daily U-100 dose
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
13:32-13:51
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: One of the questions that our colleagues wondered about was whether giving the insulin twice a day versus three times a day might be better. This trial gave us the answer. Both were very effective at lowering the A1C with really no difference between the two.
Caption: Determining Starting Dose: BID or TID?
Caption: Chapter 9
Caption: Robert Hood, Clinical Investigator of the Humulin R U-500 Study
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
13:51-14:11
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: When thinking, "How should I dose U-500?" with my patients, we have good options with both BID and TID dosing. Individualizing that for the patients is partially based on lifestyle and what choices they need on a daily basis. This gives me flexibility to decide what regimen best meets the needs of each individual patient.
Caption: Dr. Lowell Schmeltz, Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
14:11-14:37
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: From the standpoint of the distribution of insulin at the time of initiation, we looked at both published data, expert opinion, as well as computer modeling based on the pharmacodynamic properties of U-500 insulin and determined that for BID dosing, starting out with 60% in the morning and 40% in the evening would be a reasonable starting point.
Caption: BID Dose Proportions*: Before Breakfast 60%; Before Dinner 40%
Caption: *Once the dosing proportions were calculated from the U-100 total daily dose, physicians rounded down the initial dose to the nearest increment of 5.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
14:37-15:08
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: This data was also used to come up with the 40, 30, 30 distribution for the TID patients. One of the really nice things about this trial is that at endpoint the TID and BID distribution was uncannily very, very similar to the starting point. So, the fact that the broad distribution of insulin didn't change during the trial really validates the 60, 40 or the 40, 30, 30 distribution at the time of transition.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
15:08-15:28
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo appears on-screen before a table with text below and to the right of it appears on screen]
Narrator: In a clinical trial, Humulin R U-500 lowered A1C using two or three injections a day for patients uncontrolled with high-dose U-100 insulin.
Caption: Titration
Caption: Chapter 10
Caption: Table heading: A treat-to-target dosing algorithm with 2 or 3 injections of U-500 per day
Caption: TID Initial Dose Proportions: 40:30:30
| INSULIN DOSE TO ADJUST | PLASMA-EQUIVALENT GLUCOSE VALUE* | SMPG (mg/dL) | DOSE TITRATION† |
| | | ≤70‡ | -10% |
| PRE-BREAKFAST | MEDIAN§ PRE-LUNCH SMPG | 71-130 | No change in dose |
| PRE-LUNCH | MEDIAN§ PRE-DINNER SMPG | 131-180 | +5% |
| PRE-DINNER | MEDIAN§ PRE-BREAKFAST SMPG | 181-220 | +10% |
| | | >220 | +15% |
Caption: Both doses of the BID regimen were titrated; only 2 of 3 TID doses were titrated (those most needing adjustment)
Caption: Dose reductions were prioritized over dose increases for hypoglycemia
Caption: U-500 dosing was recommended 30 minutes before meals
Caption: SMPG = self-monitored plasma glucose.
Caption: *Patients should check their blood glucose before each meal and at bedtime daily, and at 3 AM if they have increased their dose in the last 48 hours.
Caption: †Used conventional rounding to nearest 5-unit increment.
Caption: ‡10% dose reduction if any pre-mealtime median, bedtime median, or single 3 AM SMPG ≤70 mg/dL.
Caption: §Median of 3 most recent daily SMPG readings.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500: Hypoglycemia
Caption: Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction associated with insulins, including Humulin R U-500. Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures, may be life-threatening, or cause death.
Caption: Increase monitoring with changes to insulin dosage, co-administered glucose-lowering medications, meal patterns, physical activity, and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment or hypoglycemia unawareness. To minimize risk of hypoglycemia, do not administer Humulin R U-500 intravenously, or dilute or mix with other products, including other insulins.
Caption: Patients and caregivers must be educated to recognize and manage hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an essential role in the prevention and management of hypoglycemia. In patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and patients who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia, increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring is recommended.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
15:28-15:48
[A table appears with text below and to the right of it]
Narrator: The doses were titrated based on the self-monitored plasma glucose levels. Dose reductions were prioritized over dose increases for hypoglycemia. These algorithms were used to titrate patients in the trial and can be found at humulin.com.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500
Caption: Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: Table heading: A treat-to-target dosing algorithm with 2 or 3 injections of U-500 per day.
Caption: BID initial dose proportions: 60:40
| INSULIN DOSE TO ADJUST | PLASMA-EQUIVALENT GLUCOSE VALUE* | SMPG (mg/dL) | DOSE TITRATION† |
| | | ≤70‡ | -10% |
| PRE-BREAKFAST | MEDIAN§ PRE-DINNER SMPG | 71-130 | No change in dose |
| | | 131-180 | +5% |
| PRE-DINNER | MEDIAN§ PRE-BREAKFAST SMPG | 181-220 | +10% |
| | | >220 | +15% |
Caption: Both doses of the BID regimen were titrated; only 2 of 3 TID doses were titrated (those most needing adjustment)
Caption: Dose reductions were prioritized over dose increases for hypoglycemia
Caption: U-500 dosing was recommended 30 minutes before meals
Caption: SMPG = self-monitored plasma glucose.
Caption: *Patients should check their blood glucose before each meal and at bedtime daily, and at 3 AM if they have increased their dose in the last 48 hours.
Caption: †Used conventional rounding to nearest 5-unit increment.
Caption: ‡10% dose reduction if any pre-mealtime median, bedtime median, or single 3 AM SMPG ≤70 mg/dL.
Caption: §Median of 3 most recent daily SMPG readings.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
15:48-16:14
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: A titration protocol is very important for any type of insulin therapy, but I think especially when using U-500 insulin because we're using much higher doses of insulin than clinicians typically have used in the past. Prior to this trial, all we really had was clinical experience, sets of patients looked at retrospectively. And that doesn't give us as good answers as a rigorous prospective trial.
Caption: Robert Hood, MD, FRCPC, FACE; Director, Endocrine Clinic of Southeast Texas; Clinical Investigator of the Humulin R U-500 Study
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
16:14-16:33
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: Historically, clinicians would look at blood sugars after the initiation and make a best guess at either raising or lowering the dose. So having data supporting a titration algorithm with the main purpose of minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia and then a secondary goal of improving blood sugars is a wonderful tool to have.
Caption: Lowell Schmeltz, MD, FACE; Assistant Professor, Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine; Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism; Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
16:33-16:56
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: So, this trial was very structured. It gave baseline characteristics, a way of transitioning the patient, a way of titrating the patient. And then very importantly what happened to these patients, both from the standpoint of efficacy, and very importantly, safety. The titration protocol during the trial took into account that U-500 insulin has both a basal and a prandial component.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
16:56-17:59
Dr. Hood: For the people on TID insulin, they adjusted their breakfast insulin based on the lunchtime blood sugar, and their lunchtime insulin based on the blood sugar taken before the evening meal. Both groups adjusted the insulin given before the evening meal based on the breakfast blood sugar the next morning. For the people on BID insulin, they adjusted their breakfast insulin based on the blood sugar check before the evening meal. From the standpoint of the actual changes, the percent changes were based on the blood sugar. So, the higher you were about the goal of 70 to 130, the greater the percentage increase. If hypoglycemia occurred, the dose reduction trumped any dose increases that might have been predicted from the protocol. For example, if you're on a BID dosing regimen and your blood sugar was high before the evening meal, but you had a low blood sugar at lunchtime, your morning insulin dose would have been decreased, not increased. This is very important from the standpoint of safety when titrating the U-500 insulin.
Caption: Table: Determine When to Adjust Dose. Check median self-monitored plasma glucose pre-lunch for the next day’s breakfast dose if on a three-times-daily dosing regimen. Check median self-monitored plasma glucose pre-dinner for the next day’s lunch dose if on a three-times-daily dosing regimen or for the next day’s breakfast dose if on a two-times-daily dosing regimen. Check median self-monitored plasma glucose pre-breakfast or at bedtime for the next day’s dinner dose for both three-times-daily and two-times-daily dosing regimens. If dose was increased within the last 48 hours, instruct patients to test for nocturnal hypoglycemia at 3 AM. Study conducted with a U-100 insulin syringe and Humulin R U-500 vial.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
17:59-18:33
[Dr. Jackson talks to camera]
Dr. Jackson: In designing the TID and BID dosing algorithms, we could have opted for adjusting by 5 or 10 or 15 units or whatever, but the problem with that is these patients were on 201 to 600 units a day of U-100 insulin. And so we adjusted by 5 to 15% for persisting hyperglycemia and we cut back by 10% per dose for hypoglycemia.
Caption: Jeffrey Jackson, MD, FACE, CDE
Caption: Over 200 units per day
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
18:33-19:04
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: So, given the wide range of doses of insulin, it would be very problematic to do a fixed change from the standpoint of number of units versus a percentage. Imagine if patient X is just taking 60 units with a meal and patient Y is taking 120 units with a meal, five units may not make much difference with one versus the next. So, we decided to go with the percentage change as opposed to a number-of-units change when titrating the U-500 insulin in this trial.
Caption: +15%; +10%; +5%; 0%; -10%
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
19:04-19:19
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: Having an algorithm that is based on percentages means you know what to do with every patient. By that, I mean that it doesn't matter if they're on 100 units of U-500 twice a day or 300 units, you know how to make adjustments in every single patient.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
19:19-19:40
[Dr. Jackson talks to camera]
Dr. Jackson: Having real evidence, randomized clinical trial evidence, I think it's going to make a tremendous difference in reassuring physicians that they have a good idea of how to use U-500, how to start it, how to titrate it, and what results they may be able to achieve.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
19:40-20:34
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo; Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera; Humulin R U-500 KwikPen rotates into view, with the dose indicator turning to various dose selections]
Dr. Schmeltz: For many years, we lived in a U-100 world where patients were on insulin pens. And the only insulin that you had to use a vial and a syringe was Humulin R U-500. Having a pen now is really going to reduce that barrier and I believe patients are going to be much more willing to go on a more concentrated insulin like U-500, knowing that it's the similar device to what they've been taking all along. Patients are familiar with the pens, I'm familiar with the pens, and we don't have to do this dose conversion anymore. If I tell someone to take 100 units of Humulin R U-500, they're gonna be able to dial this all the way up to 100 units, and I know confidently they're going to be able to inject it and administer it.
Caption: Starting with the U-500 KwikPen®
Caption: Chapter 11
Caption: Dr. Lowell Schmeltz, Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: No dose conversion
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
20:34-20:43
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: From my standpoint, I appreciate the better accuracy of a pen delivery system as opposed to relying on a patient to draw up insulin in an accurate fashion.
Caption: Dr. Robert Hood, Director, Endocrine Clinic of Southeast Texas
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
20:43-21:08
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: Healthcare professionals are very comfortable with insulin dosing in the pens because there is no dose conversion needed and a unit of insulin is a unit of insulin. In the U-500 world, we sort of went backwards with the vial and syringe and many clinicians, instead of talking in total units per injection, they spoke in volume and unit equivalence or unit markings on a syringe.
Caption: U-500 KwikPen
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
21:08-21:15
[Humulin KwikPen animates with dose indicator turning to illustrate different doses]
Dr. Schmeltz: So, it's really important to re-educate the patient of the total units that they're taking with each injection rather than focusing on the volume.
Caption: 100 units dialed = 100 units of insulin
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
21:15-21:33
[Dr. Hood talks to camera; image of KwikPen on screen]
Dr. Hood: So, before the KwikPen, you had this translation issue. With the KwikPen, you have no issue at all. All the patient sees is units, and that's really what insulin therapy is all about. It's gonna be a lot nicer delivery system than what we've had in the past.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
21:33-21:55
[Humulin KwikPen rotates on screen, with dose adjustments being reflected in the dose window; Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera; arrow points to a KwikPen dose window, illustrating dose selections]
Dr. Schmeltz: With the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen now, teaching Humulin R U-500 is way easier. Just as they would dial the total units up on a Humalog pen, for example, now they can dial the total number of units up on the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen and show the patient how to administer it.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: Dial and dose
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
21:55-22:09
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo appears on-screen; Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: One of the problems with high-dose insulin therapy is if you have a pen, you can't deliver all the insulin you need with a single injection, and the pen itself doesn't hold very much insulin so you use the pen up very quickly.
Caption: U-500 KwikPen® Features
Caption: Chapter 12
Caption: Dr Robert Hood, Director, Endocrine Clinic of Southeast Texas
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
22:09-22:20
[Humulin KwikPen rotates on screen while Dr. Hood speaks, with doses adjustments being reflected in the dose window]
Dr. Hood: This pen can deliver up to 300 units with a single injection and carries 1500 units per pen. Having the U-500 in a KwikPen to me is really a major development.
Caption: Up to 300 units in one injection; 1500 units in a single pen
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
22:20-22:33
[Humulin KwikPen rotates on screen next to Dr. Schmeltz]
Dr. Schmeltz: You can give up to 300 units on a single injection and that's the most amount of insulin that you can give on any device currently on the market. For patients who need so much insulin every day, it's nice to have a pen that's made for them.
Caption: Up to 300 units in one injection
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
22:33-22:52
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: Patients often react negatively as we escalate the insulin dose, and they often are looking at the volume of insulin given as opposed to the actual number of units. It's nice that they're able to package the U-500 into a KwikPen that's no different in size than the other KwikPen devices.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
22:52-23:08
[Animated Humulin KwikPen next to Dr. Hood speaking]
Dr. Hood: So, having a pen that's the same size as the other pens, you're not dealing with this big monster of a pen. That's important. They've been able to package a lot more insulin into a platform that's going to be very patient friendly.
Caption: Same size as other KwikPens
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
23:08-23:17
[Animated Humulin KwikPen next to Dr. Schmeltz speaking]
Dr. Schmeltz: The Humulin R U-500 KwikPen is an aqua color, and by being distinctly different from the other insulin pens on the market, the risk of confusion or error with other insulins is minimal.
Caption: Aqua color differentiation
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
23:17-23:30
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: It is absolutely vital that a patient gets the insulin that we're prescribing. Having a distinctive pen color is very important for U-500 patients so they can look at the pen and say, "Yes, this is U-500."
Caption: Aqua color differentiation
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
23:30-23:42
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo appears on screen; an example image of prescription pad with prescribing details filled in]
Narrator: After you've written the prescription, discussing what patients should expect with U-500 can go a long way in helping them get started.
Caption: Getting Patients Started
Caption: Chapter 13
Caption: Prescribing and the pharmacy
Caption: Example prescription: The prescription details should be individualized and determined, by the prescriber, in accordance with the needs of the patient.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Caption: Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
23:42-23:52
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: And, so, it is a change in the way that they go about their daily business, having to take insulin monotherapy rather than multiple different types of insulin on a daily basis.
Caption: Lowell Schmeltz, MD, FACE; Assistant Professor, Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine; Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
23:52-24:15
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: When seeing patients back at their first follow-up visit after starting U-500, they often have a big smile on their face and they tell me, “You finally found a drug that works for me.” They're seeing better blood sugar numbers, they're taking fewer injections a day, and they report to me that they're more satisfied with their diabetes care.
Caption: Trial participants experienced:
Caption: Lower A1C
Caption: Fewer injections*
Caption: Reduced volume*
Caption: Similar rates of severe hypoglycemia (TID and BID)†
Caption: *Compared to U-100 insulin. Most patients will require 2 or 3 daily injections of U-500.
Caption: †All hypoglycemia analyses were performed using the full analysis set defined as all randomized patients receiving at least one dose of study drug.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
24:15-24:44
[Dr. Hood walks into frame, sits down, and begins talking; Animated aqua blue circles representing units of insulin bounce around inside a rectangular box; the box compresses in size, pushing the same number of blue circles closer together]
Dr. Hood: When I initiate a patient on Humulin R U-500 insulin, I emphasize that it is a more concentrated insulin, but that a unit of U-500 is the same as U-100 insulin. It's simply compacted into a smaller volume. That smaller volume translates into fewer injections and smaller volumes of insulin per injection. And because U-500 has both long- and short-acting components, they can get by with just one type of insulin to help control their blood sugars.
Caption: Robert Hood, MD, FRCPC, FACE; Director, Endocrine Clinic of Southeast Texas; Clinical Investigator of the Humulin R U-500 Study
Caption: 10 units of U-100 insulin
Caption: 10 units of U-500 insulin
Caption: 80% less volume*
Caption: *Compared to U-100 insulin.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
24:44-25:08
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera; animated syringes drop from the top to the bottom of the screen and then out of sight, illustrating the many syringes used by a person needing high doses of insulin; falling syringes settle on just two syringes]
Dr. Schmeltz: Patients requiring high-dose insulin, over 200 units a day, are often taking 5, 6, even up to ten injections a day. To offer a two- or three-time-a day injectable insulin, the patient's eyes light up and they're very excited to try a different insulin that allows them to get the entire total daily dose of insulin they need in only two or three injections.
Caption: Dr. Lowell Schmeltz, Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is given two or three times daily before meals.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
25:08-25:28
[Dr. Hood talks to camera]
Dr. Hood: We then talk about how we're going to transition them from the U-100 to the U-500 insulin. We talk about how we're going to titrate the insulin. We discuss blood sugar monitoring frequency. We review hypoglycemia and we also discuss with the patient when they're going to be contacting us to help adjust therapy.
Caption: Key patient discussion points
Caption: Blood sugar monitoring
Caption: Hypoglycemia
Caption: Adjusting therapy
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
25:28-25:57
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: It's absolutely critical that they keep a blood sugar log or bring their blood sugars to the office for us to review so that we can safely adjust it to make sure we're achieving our targets while also not having significant hypoglycemia. Ideally, they're taking their insulin injection 30 minutes prior to the meal. So, if they're on BID, that's 30 minutes before breakfast and 30 minutes before dinner. If they're on a TID dose, then it would be 30 minutes before breakfast, lunch, and dinner.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
25:57-26:17
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo appears on screen; Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: For the vast majority of my patients, cost is a concern. They want to maintain, as best as possible, their blood sugar control and their self-management. However, cost is a consideration.
Caption: Affordability
Caption: Chapter 14
Caption: Dr Rosemarie Lajara, Endocrinologist, Diabetes Centers of America – DFW
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
26:17-26:25
[Dr. Jonathan Marquess talks to camera]
Dr. Marquess: Cost of medication is something we talk about every single day, and our pharmacists do a really good job educating the patient about the medication.
Caption: Jonathan G. Marquess, PharmD, CDE; President and CEO, The Institute for Wellness and Education
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
26:25-26:53
[Graphic of a prescription sheet with a blue checkmark; Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: In this day and age, most people are much influenced by formulary status because obviously there is a cost to medications and our patients take several medications, not just the insulin. When I'm starting a patient on U-500, I do check to see whether it's covered under their formulary and try to find means of providing the insulin with the lowest cost possible for my patient population.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
26:53-27:02
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: So, in starting Humulin R U-500, I definitely discuss that being on one insulin as both basal and mealtime versus being on two insulins.
Caption: Dr. Lowell Schmeltz, Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
27:02-27:22
[Image of a calendar page with the number 1 in the middle, Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: I usually discuss that now instead of having two co-pays for two separate insulins, they will only have that one co-pay for the U-500. And obviously, I go over the number of pens that they will receive, based on the total daily units and how that may impact their co-pays and the insulin cost.
Caption: 1 insulin co-pay
Caption: Patients transitioning from U-100 basal-bolus therapy to U-500 as insulin monotherapy may have fewer co-pays.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
27:22-27:34
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: The co-pay is certainly an advantage in that there'll be having fewer co-pays. But most patients are eager to switch over to a simpler regimen with a single kind of insulin.
Caption: Dr Ralph Goodman, Endocrinologist, Sacred Heart Medical Group
Caption: U-500 may reduce the number of daily injections compared to standard U-100 insulin
Caption: Most patients will require 2-3 injections of U-500 a day
Caption: Patients can inject up to 80% less liquid and still get the dose they need.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
27:34-27:56
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: When my patients go to the pharmacy to pick up their U-500 prescription, I usually provide them a savings card. I want to make sure that they can utilize it at the pharmacy. Most of my patients are very pleasantly surprised and enthusiastic about the potential cost savings utilizing the savings card.
Caption: Savings cards are available at humulin.com*
Caption: *For eligible, commercially insured patients.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
27:56-28:17
[Dr. Hood speaks to camera]
Dr. Hood: With these very high-insulin-dose patients, if they have a plan where it's a percentage of the cost of the insulin, the high number of units makes insulin a very expensive medication. Limiting this to a fixed co-pay, that in the big scheme of things is fairly modest for what they're getting therapeutically, can be very helpful for my patients.
Caption: Dr. Robert Hood, Clinical Investigator of the Humulin R U-500 Study
Caption: See humulin.com/save for terms and conditions*
Caption: *For eligible commercially insured patients
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
28:17-28:42
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: So, comparatively, unit-per-unit, U-500 is less expensive than other basal or bolus analogs. Of course, a 20-milliliter vial is going to be more expensive, but we have to keep in mind that that contains as much insulin as ten vials of U-100, and that a KwikPen has as much insulin as a whole box of five pens of U-100 insulin.
[Graphic of a down-pointing arrow with a label “$ Cost per unit” (AnalySource.com as of 01/2018), depicting “lower cost per unit.”]
[Animation of Humulin R U-500 KwikPen bounces into view]
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
28:42-28:51
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: As an endocrinologist, I understand that you can have the best medication in the world, but if it's not utilized, you cannot get the results you want.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
28:51-29:11
[Light music accompanies chapter transition; Humulin R U-500 logo appears on-screen; Dr. Lajara talks to camera]
Dr. Lajara: There is a learning curve and a comfort level that needs to be acquired. That starts obviously at the office with the office visit, with the provider, but it continues as the patients go to the pharmacy to get their first prescription.
Caption: At the Pharmacy
Caption: Chapter 15
Caption: Dr. Rosemarie Lajara, Endocrinologist, Diabetes Centers of America – DFW
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
29:11-29:29
[Dr. Goodman talks to camera]
Dr. Goodman: When we're changing from a basal-bolus therapy to U-500, it's important for the pharmacist to understand that the patient will no longer be dispensed any of their prior insulins. And I also make it perfectly clear to the patient that they are to no longer take any of their U-100 insulin once they start U-500.
Caption: Dr Ralph Goodman, Endocrinologist, Sacred Heart Medical Group
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 – Contraindications
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
29:29-29:46
[Graphics of a telephone and a pharmacist’s mortar and pestle next to Dr. Schmeltz]
Dr. Schmeltz: When initially prescribing Humulin R U-500, it's important to discuss with the patient that this is an insulin not often stocked at pharmacies. And so to call the pharmacy ahead of time and let them know you're bringing a script in for Humulin R U-500, the pharmacy has the ability to get it in stock before you go and pick it up.
Caption: Dr. Lowell Schmeltz, Chief, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Detroit Medical Center Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
29:46-30:01
[Dr. Marquess talks to camera]
Dr. Marquess: This is the great thing about pharmacists is we have a relationship with the patient. He may have been with my pharmacy for ten years. That will help me more to understand that patient, but also to understand their new U-500 prescription and how it's going to impact their life.
Caption: Jonathan G. Marquess, PharmD, CDE, President and CEO, The Institute for Wellness and Education
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
30:01-30:18
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera; Image of Humulin KwikPen]
Dr. Lajara: The most common question that I get from the pharmacist is usually related to the doses. Since a unit is a unit, when they see the amount of insulin that my patients are taking, they tend to question whether that's the amount of insulin that I intended to prescribe.
Caption: 1 unit = 1 unit
Caption: No dose conversion
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
30:18-30:42
[Dr. Marquess talks to camera; Humulin R U-500 KwikPen with numbers rotating inside the dose window]
Dr. Marquess: With diabetes, a patient has a lot to think about. We want to make sure that they understand how, when, and why they're taking this U-500 insulin and how to operate the pen. We will give the specific example of let's dial up to 100 units because this is what you're going to do tomorrow morning, and we like to see the patient actually dial it up to the 100.
Caption: 100 units dialed = 100 units of insulin
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Adverse Reactions
Caption: Adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
30:42-31:00
[Dr. Lajara talks to camera; graphic of a calendar page with “month” at the top and weekly grid below]
Dr. Lajara: Once I start a patient on U-500 insulin, I do stay in close touch with them, in the first few weeks especially, because I want to make sure that they're understanding how to administer it and how to monitor their blood sugar, so there are no errors involved in the use.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Drug Interactions
Caption: Some medications may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment. Please see the Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information for a list of drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Particularly close glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with drugs such as antiadrenergic agents that can alter the signs of hypoglycemia.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
31:00-31:17
[Dr. Schmeltz talks to camera]
Dr. Schmeltz: At their first follow-up visit after starting U-500, they often have a big smile on their face, and they tell me, “You finally found a drug that works for me.” They're seeing better blood sugar numbers, they're taking fewer injections a day, and they report to me that they're more satisfied with their diabetes care.
Caption: Select Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 - Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: See Important Safety Information at the end of this video and accompanying Full Prescribing Information.
31:17-40:38
[Important Safety Information for Humulin U-500 scrolls up the screen while the Humulin R U-500 logo is in the bottom right corner]
Caption: Chapter 16: Important Safety Information
Caption: Important Safety Information for Humulin® R U-500 (insulin human) injection
Caption: Humulin R U-500 is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Humulin R U-500 or any of its excipients.
Caption: Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia, or Death Due to Dosing Errors With Vial Presentation can be life-threatening. Overdose has occurred as a result of dispensing, prescribing, or administration errors. Attention to details at all levels is required to prevent these errors.
Patients should be prescribed U-500 syringes for use with Humulin R U-500 vials. Do not use any other type of syringe to administer Humulin R U-500.
If using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®, patients should be counseled to dial and dose the prescribed number of units of insulin.
Do NOT perform dose conversion when using the Humulin R U-500 KwikPen or U-500 insulin syringe.
Caption: DO NOT transfer Humulin R U-500 from the KwikPen into any syringe for administration. Overdose and severe hypoglycemia can occur.
Caption: Never share a KwikPen or U-500 syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed, to avoid risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Caption: Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia With Changes in Insulin Regimen
Caption: Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Any changes in insulin regimen should be made cautiously and only under close medical supervision, and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Due to reports of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to the unaffected areas and to closely monitor blood glucose. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant anti-diabetic products may be needed.
Caption: Hypoglycemia
Caption: Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction associated with insulin, including Humulin R U-500. Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures, may be life-threatening, or cause death.
Caption: Increase monitoring with changes to insulin dosage, co-administered glucose-lowering medications, meal patterns, physical activity, and in patients with renal or hepatic impairment or hypoglycemia unawareness. To minimize risk of hypoglycemia, do not administer Humulin R U-500 intravenously, intramuscularly, or in an insulin pump or dilute or mix with other products, including other insulins.
Caption: Patients and caregivers must be educated to recognize and manage hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an essential role in the prevention and management of hypoglycemia. In patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and patients who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia, increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring is recommended.
Caption: Hypersensitivity Reactions
Caption: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulins, including Humulin R U-500. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue Humulin R U-500; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve.
Caption: Hypokalemia
Caption: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated.
Caption: Fluid Retention and Heart Failure With Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Caption: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause dose-related fluid retention when used in combination with insulin. Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure and consider reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs.
Caption: Adverse Reactions
Caption: Other adverse reactions include allergic reactions, lipodystrophy, injection site reactions, pruritus, and rash.
Caption: Drug Interactions
Caption: The following drugs may alter glucose metabolism and may necessitate insulin dose adjustment:
Caption: Drugs that may increase the risk of hypoglycemia: antidiabetic agents, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blocking agents, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, pentoxifylline, pramlintide, salicylates, somatostatin analog (e.g., octreotide), and sulfonamide antibiotics.
Caption: Drugs that may decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500: atypical antipsychotics (e.g., olanzapine and clozapine), corticosteroids, danazol, diuretics, estrogens, glucagon, isoniazid, niacin, oral contraceptives, phenothiazines, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives), protease inhibitors, somatropin, sympathomimetic agents (e.g., albuterol, epinephrine, terbutaline), and thyroid hormones.
Caption: Drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500: alcohol, beta-blockers, clonidine, and lithium salts. Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be followed by hyperglycemia.
Caption: Increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when Humulin R U-500 is co-administered with the following drugs:
Caption: Drugs that may increase the risk of hypoglycemia: antidiabetic agents, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blocking agents, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, pentoxifylline, pramlintide, salicylates, somatostatin analog (e.g., octreotide), and sulfonamide antibiotics.
Caption: Drugs that may decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500: atypical antipsychotics (e.g., olanzapine and clozapine), corticosteroids, danazol, diuretics, estrogens, glucagon, isoniazid, niacin, oral contraceptives, phenothiazines, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives), protease inhibitors, somatropin, sympathomimetic agents (e.g., albuterol, epinephrine, terbutaline), and thyroid hormones.
Caption: Drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Humulin R U-500: alcohol, beta-blockers, clonidine, and lithium salts. Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be followed by hyperglycemia.
Caption: Drugs that may blunt signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia: beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine, and reserpine.
Caption: HM U500 HCP ISI 02FEB2023
Caption: For more information, see Full Prescribing Information, including Patient Information and Instructions for Use for the KwikPen and vial.
Caption: PP-HM-US-2040 07/2023 ©Lilly USA, LLC 2023. All rights reserved.